Dosbox Use Serial Port
IPXNET CONNECT opens a connection to an IPX tunneling server running on another DOSBox session. The 'address' parameter specifies the IP address or host name of the server computer. You can also specify the UDP port to use. By default IPXNET uses port 213 - the assigned IANA port for IPX tunneling - for its connection.
- Dosbox Use Serial Port
- Dosbox Use Serial Port Gigabit
- Dosbox Use Serial Port Replicator
- Dosbox Use Serial Port Arthur
How do I configure Printfil to capture DosBox printjobs ?DOSBOX is a DOS emulator, freely available at http://www.dosbox.com - Some Customers do use it to run their DOSprograms; mainly on 64 bit Windows systems (that cannot run 16 bitsoftware, like DOS, natively). Howto configure Printfil to capture DOS print jobs run inside DosBox dependsmainly by how the DOS program itself produces those jobs:
1) The DOSprogram 'prints to file' itself /ace-ventura-movie-download-for-mobile.html. Inthis case you just have to point Printfil to the very same file nameproduced by the DOS program. Youcan do it by inserting that file name in the 'File to check'field at Configuration -> Standard Assoon as the DOS program finishes printing, Printfil will capture thejob-file and will show it on screen, if Preview isenabled at Configuration -> Standard, orwill directly send it to the choosen Windows printer. 2) The DOSprogram prints to parallel ports (LPT1:, LPT2:, LPT3:) or serial ports (COM1:, COM2:, COM3:, COM4:) Inthis case please note that the Standard DosBox buildavailable at the link above does NOT support parallel portemulation, so, print jobs sent by a DOS program to (say)LPT1: in DosBox simply 'disappears' and Printfil receives nothing tocapture, even if you've selected the LPT1: port at Configuration-> Standard . There arehowever special DosBox builds (DosBox SVN Daum and DosBox MegaBuild)that DO support parallel port emulation NEW: If instead you already have DOSBox up and running on your machine, the newer Printfil version automatically detects if DosBox SVN Daum or DosBox MegaBuild isinstalled on your Windows machine when selecting aLPT port to capture at Configuration -> Standardand asks you if you want to automatically configure DosBox to capture the selected COM port or LPT port. So, in order to capture print jobs sent to the LPT1: , LPT2: , LPT3: , COM1: , COM2: , COM3: or COM4: portby a DOS program within DosBox you just have to:
If you prefer to redirect DOSBox prints to Printfil without using the standard configuration dialog, you can do it by the command line parameters from the Windows Command Prompt as described in the article: How to make Printfil capturing prints in DOSBox | |
DOS PRN USBFAQSee also .. | |
Login screen for Digital Distortion BBS as seen in Telemate under DOSBox.
A few months ago I wrote about my experiences trying to telnet in to Atari BBSes using an emulated Atari on my Mac.
Basically the solution boiled down to this: Use tcpser4j to change a telnet connection to a serial connection, use socat to pipe that serial connection to a file, and set the Hatari emulator to use that file as a virtual RS232 device. After those steps, I could run my favorite old Atari ST terminal programs like ANSIterm and Freeze Dried Terminal.
Recently I decided I wanted to do the same thing with a DOS emulator like DOSBox — but for different reasons.
What I wanted to try this time were DOS front-end programs for BBS door games like Global War, Land of Devastation, and TradeWars. These front-ends work only in DOS, and each one is unique. They offer special features like EGA or SVGA graphics or sound effects. I’ll write more about these front-ends in the near future.
Setting up DOSBox
Before I could do try using front-ends, first I had to learn how to telnet from a regular terminal program on an emulated PC.
Turns out that it’s really easy. And the folks at StarBase 21 BBS have already written a great tutorial on how to do it.
Basically, you don’t need anything except DOSBox! No socat. No tcpser. DOSBox has its own built-in routines for piping a telnet connection through its virtual serial port.
I’ll condense the SB21 instructions (and clarify one detail for Macs), in case you’d like to try this yourself:
1. Download a copy of Telemate or Telix or whatever DOS terminal program you want
2. Download a copy of the latest version of DOSBox for your platform (for me, Mac OS X)
3. Install DOSBox on your machine. This is fairly easy, but if you get stuck you can find help on the DOSBox wiki
4. Edit the config files in a text editor like Notepad, Sublime Text, Text Edit, etc. As the SB21 tutorial explains, the location of the file varies by platform:
Windows XP: %USERPROFILE%Local SettingsApplication DataDOSBoxdosbox-#.##.conf
Windows Vista / 7: {system drive}:Users{username}AppDataLocalDOSBoxdosbox-#.##.conf
Mac OS X: {username}/Library/Preferences/DOSBox #.## Preferences
Dosbox Use Serial Port
(Please note that the SB21 tutorial is slightly mistaken about OS X. On the Mac it is not a .conf file)
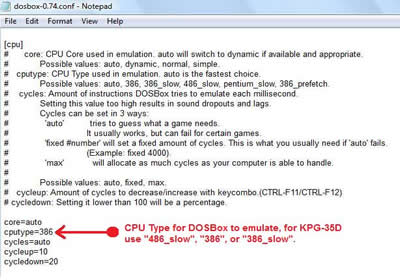
4a. Go to the “serial” section beginning on line 199 and change these two lines:
to
4b. Go to the “autoexec” section beginning on line 239 and add a mount instruction. This will tell DOSBox to use a folder on your computer as a hard drive for the emulated DOS PC.
If you’re on Windows, you might put this:
On a Mac, you might put this:
Dosbox Use Serial Port Gigabit
Save and close the config file after making this change.
5. On your computer, create that “dos” folder at the location you specified in step 4b.
6. Unzip the terminal program you downloaded in step 1 into the dos folder you created in step 5.
7. Run DOSBox. You should now be able to launch your terminal program! Be sure to change the baud rate to the highest available speed.
8. To telnet to a BBS, just type old Hayes “AT” modem commands into the terminal — but with a telnet address instead of a phone number. For example:
Dosbox Use Serial Port Replicator
You should be golden!